[Doctor-supervised] How to choose the right bed

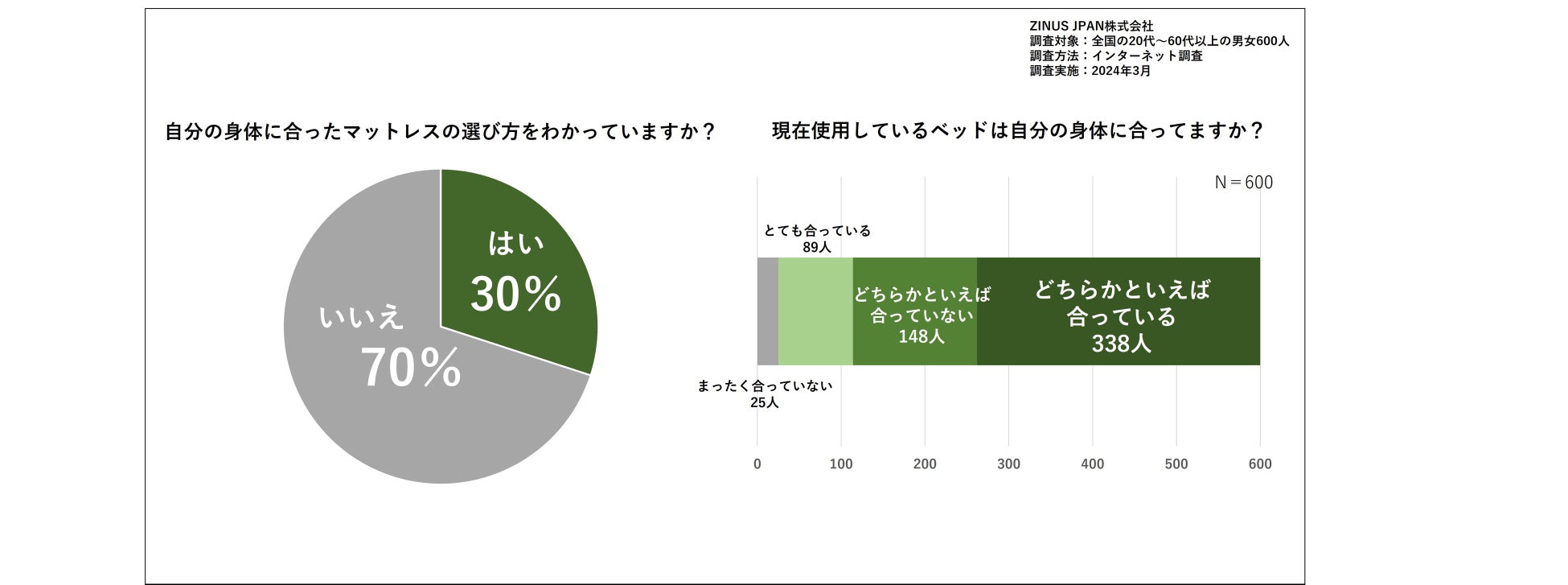
70% of people don't know how to choose a mattress
In preparation for World Sleep Day on March 15th, ZINUS conducted a survey of 600 men and women in their 20s to 60s across the country regarding the bed mattresses they currently use.
The survey results showed that 70% of people answered that they "don't know how to choose a mattress that suits their body," and 28% answered that "the bed they are currently using does not suit their body." Many people do not know how to choose a bed mattress, and in fact, just under 30% of people end up purchasing a mattress that does not suit their body.
There are countless options for bed mattresses, but choosing one based on intuition can result in an uncomfortable sleep or even increased fatigue. However, choosing a bed mattress that suits your body can help reduce pain and discomfort, and even help you feel more active in the morning.
We will explain how to choose the right mattress that suits your body type and environment, as well as the types of beds, from the perspective of doctors and bed mat professionals.
[Supervision]

Orthopedic surgeon Dr. Kiyonori Tomiwa
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tankita Hospital, Tankita Social Medical Corporation.
Graduated from the Faculty of Medicine, Iwate Medical University. Doctor of Medicine, specialist of the Japanese Orthopaedic Association, Japan DMAT doctor, sports doctor certified by the Japan Sport Association, and industrial physician. Particularly knowledgeable in cycling, he has worked as a race doctor and is also an elite national commissaire from the International Cycling Union. Editorial committee member of Bicycle City (Rising Publishing).

Advanced Sleep Health Instructor Ayato Takano
An expert on mattresses and sleep, he has purchased and tried over 50 mattresses in a year. He helps many people choose bedding and mattresses from the perspective of sleep quality and QOL.
Good Sleep Hack: https://gsleep-hack.site/
According to a 2021 survey, the average sleep duration for Japanese men was 7.58 msec and for women 7.49 msec (Reiwa 3 Basic Survey on Social Life, Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications). This suggests that people generally spend roughly one-third of their 24 hours sleeping. Furthermore, whether this is an appropriate length of time is questionable. A large-scale UK study reported that 7-9 hours of sleep was associated with the best cerebral cortex health in brain MRI scans. Similarly, a six-year follow-up of 1.1 million people found that a sleep duration of approximately 7 hours was associated with the lowest risk of death. *1 *1 Kripke DF, et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2002;59:131-6.
Generally speaking, you should aim for around 7 hours of sleep, but this is only a guideline as this varies from person to person.
Considering that we spend about 30% of our day in bed, or 30% of our lives, it's only natural that we would want to achieve high quality during that time. It is said that about half of our sleeping positions are in the supine position (lying on our backs). It is also said that we turn over in our sleep about 50 times per sleep session.
Bedding is mainly classified into "mattress," "pillow," and "quilt," and among these, mattresses are classified as "mattress." The role of "mattress" is to "maintain proper sleeping posture and distribute body pressure." The ideal condition of bedding is: -Easy to turn over in bed -Maintain a natural sleeping posture -Comfortable sleeping posture when falling asleep -Provides a sense of psychological security
It is said that the ideal situation is to fulfill these conditions.
When choosing a mattress, you can ensure better sleep by checking and selecting three points when you wake up: ease of turning over, comfort when lying on your back, and comfort when falling asleep.The ideal way to choose a mattress is to actually sleep on it and reflect on these three points when you wake up, so we recommend taking advantage of trial rental services offered by various manufacturers.
Differences in the width, hardness, and elasticity of a bed mattress can have a significant impact on the quality of sleep.
You may have heard people say that a bed with just the right amount of firmness is best, but there have also been reports of people experiencing back pain with a medium-firm bed, so it's hard to say for sure, and the bed mattress that best suits you will vary depending on your body shape and sleeping position.
Regarding the width of the bed, it's best to choose one that's wide enough to allow for easy turning over, and if possible, choose one that's as wide as possible. Turning over in bed (hereafter referred to as "turning over") is a crucial sleep activity. If you don't turn over in bed for several hours, bedsores will develop. Therefore , in medical settings, staff will reposition patients who have difficulty changing position on their own every two to four hours. Changing positions also helps to relieve muscle tension and regulate the humidity and temperature inside the futon. In other words, if it's difficult to turn over in bed, localized muscle tension will increase, worsening shoulder and back pain and making it difficult to regulate sweating.
Types of bed mattress materials
We will introduce the main types of mattress materials and the type of person they are suitable for.
・Low-resilience urethane

This is a type of urethane with a resilience modulus of less than 15%. It is available in a wide range of densities, from inexpensive to expensive. Its main feature is its soft, fluffy feel that envelops the body. It gently conforms to the body, providing a sense of relaxation. While it is comfortable to sleep on, mattresses made solely of low-resilience urethane have the disadvantage of weak support and making it difficult to turn over. Be careful, as your body will sink too much, making the mattress prone to becoming stuffy and collapsing.
Recommended for:
・People weighing less than 45 kg ・People who tend to sleep on their side
It is recommended for slender people and children who find hard materials cause pain. It is also suitable for people who often sleep on their side. When sleeping on your side, the curves around your shoulders and hips become larger than when you sleep on your back, so memory foam fits your body better.
- Urethane (general)
This refers to urethane mattresses with a resilience rate of 15-49%, neither low nor high resilience. They range from soft to hard, so it's easy to find the firmness that's right for you. Because the resilience is somewhere between low and high resilience urethane mattresses, some mattresses may make it easier to turn over in bed if the fit isn't too good.
Recommended for:
・Low resilience is too soft ・High resilience is too hard
This is recommended for people who feel that low-resilience urethane is too soft and high-resilience urethane is too bouncy.
- High resilience urethane (high elasticity)

Urethane with a resilience of 50% or more. This material is often used as filling for expensive mattresses and high-end coil mattresses. Its main features are its support and ease of turning over in bed, making it a popular mattress for relieving lower back pain. While its durability is inferior to that of coil mattresses, it is the highest of all urethanes.
By the way, be careful, as some cheap mattresses may label urethane as "high resilience" when it is simply hard. As a guideline, if you choose a mattress that costs over 30,000 yen, there is a high chance that it uses true high resilience.
Recommended for:
・Want to use it for a long time ・Prefer a firm sleeping experience
High-resilience urethane is a material that is suitable for many people because it supports turning over in bed. Many mattresses have a slightly firmer sleeping experience, which is why many Japanese people prefer it.
However, it may be too hard for skinny people under 50kg or women with strong curves.
・Bonnell coil

This mattress is made by connecting coil springs together. The connected coils support the body as a whole, making it a firmer sleeping experience. It has strong support and makes it easy to turn over in bed. Another benefit is that the coil layer is breathable. However, because the coils are all connected, weight on one area can cause other areas to sink, meaning poor body pressure distribution is a disadvantage. This material tends to concentrate pressure on the heavier parts of the body, and you can easily feel the vibrations of the person next to you.
Recommended for:
・Cost-conscious ・Prefer a fairly firm mattress ・Stout build ・Sleeping alone
・Pocket coil

This mattress has coils individually placed in small nonwoven bags and spread throughout the entire mattress. Each coil moves independently, providing point support for the body. The greatest advantage is that each coil moves independently, making it easy to conform to the slight curves of the body. It has excellent body pressure distribution, making it easier to maintain proper sleeping posture.
Another benefit is that vibrations are less likely to be transmitted, so you are less likely to be woken up by the movements of the person next to you. Even if pressure is applied to the mattress, it has less effect on the other coils. Another benefit is that the rebound force of the springs makes it easier to turn over in bed.
Although it is slightly less breathable than bonnell coil, it is more breathable than a urethane mattress and is a material with no major disadvantages.
Recommended for:
・Want to use it for a long time ・Prioritize hygiene ・Sleeping with 2 or more people
This mattress offers a good balance of comfort, ease of turning over, durability, and hygiene. It also reduces vibrations from the person sleeping next to you, making it ideal for sleeping with two or more people.
·hybrid

This multi-structure mattress combines different materials to take advantage of the benefits of each. It combines a soft feel with ease of turning over, while pocket coils compensate for the breathability and resilience that are drawbacks of low-resilience mattresses, resulting in very few drawbacks overall. It maximizes the benefits of different materials; for example, ZINUS Prime Support, which combines low-resilience urethane and pocket coils, offers a good balance of the comfort and fit of low-resilience mattresses and the resilience, breathability, and durability of pocket coils.
Recommended for:
・Want to get a good night's sleep ・Sleep in a variety of positions ・Prioritize a balance of performance
The hybrid mattress combination of "pocket coil x high-resilience urethane x low-resilience urethane" is recommended as it provides good comfort, sleeping posture, and breathability, but prices vary, so look for a hybrid mattress that fits your budget.
·latex

This mattress is made from the sap of rubber trees and has the softness and elasticity that is characteristic of rubber. There are two types: natural latex and synthetic latex.
The softness and elasticity unique to rubber makes it excellent at distributing body pressure, making it a material that makes it easy to turn over in bed.
Natural latex has natural antibacterial properties and is less susceptible to dust mites and mold. It also has the advantage of being durable. However, it also has some drawbacks, such as being heavy, having a noticeable odor, not suitable for people with latex allergies, and often being expensive.
Recommended for:
・I like a soft sleeping experience ・I want to use it for a long time ・I value hygiene
Its soft yet resilient nature makes it suitable for lighter people. Natural latex is considered a superior material. However, people with latex allergies should exercise caution when using this product, as contact between the skin and the latex proteins in natural rubber can cause skin problems such as redness, itching, and hives. Also, please note that children's ability to roll from a prone position to a supine position varies greatly, so please avoid using this product, especially infants.
Fiber

A material made from solidified resins such as polyethylene and polyester. Fiber mattresses have a three-dimensional structure with lots of air space, making them extremely breathable. They are resistant to moisture buildup and mold, so they are safe to use on the floor. Another benefit is that they have excellent resilience, meaning less force is required to turn over.
However, it is often considered too hard to sleep on, is expensive, and is a material that has mixed reviews. It is also sensitive to high heat, so those who use a futon dryer should be careful.
Recommended for:
・Want to use it directly on the floor ・Sweaty ・Stout build
Its breathability is top-notch, so it can be used hygienically for a long time. If you find it hard to sleep on, we recommend adding a thin mattress topper. It efficiently releases moisture, making it ideal for those who wake up in the middle of the night due to heat.
Tips for choosing a mattress

There are two important points to consider when choosing a mattress:
1. Hardness suited to body weight (body pressure distribution)
② Resilience that makes it easy to turn over in bed (resilience)
1. Hardness that suits your body (weight) (body pressure distribution)
The most important thing when choosing a mattress is its firmness (body pressure distribution). Using a mattress with the right firmness for your body will support your weight evenly across your entire body and allow you to sleep in a natural position. This will help reduce back pain and fatigue.
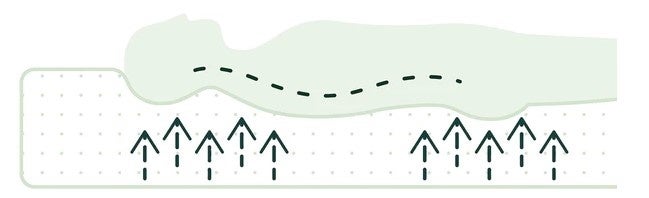
If the mattress is too hard, your hips will float up, and because your hips are not touching the mattress, body pressure will be concentrated on your buttocks and back, leading to poor circulation and muscle fatigue in those areas. Furthermore, your hips will float up, resulting in an unnatural sleeping position. This not only makes it difficult to sleep well, but can also lead to skin disorders such as bedsores.
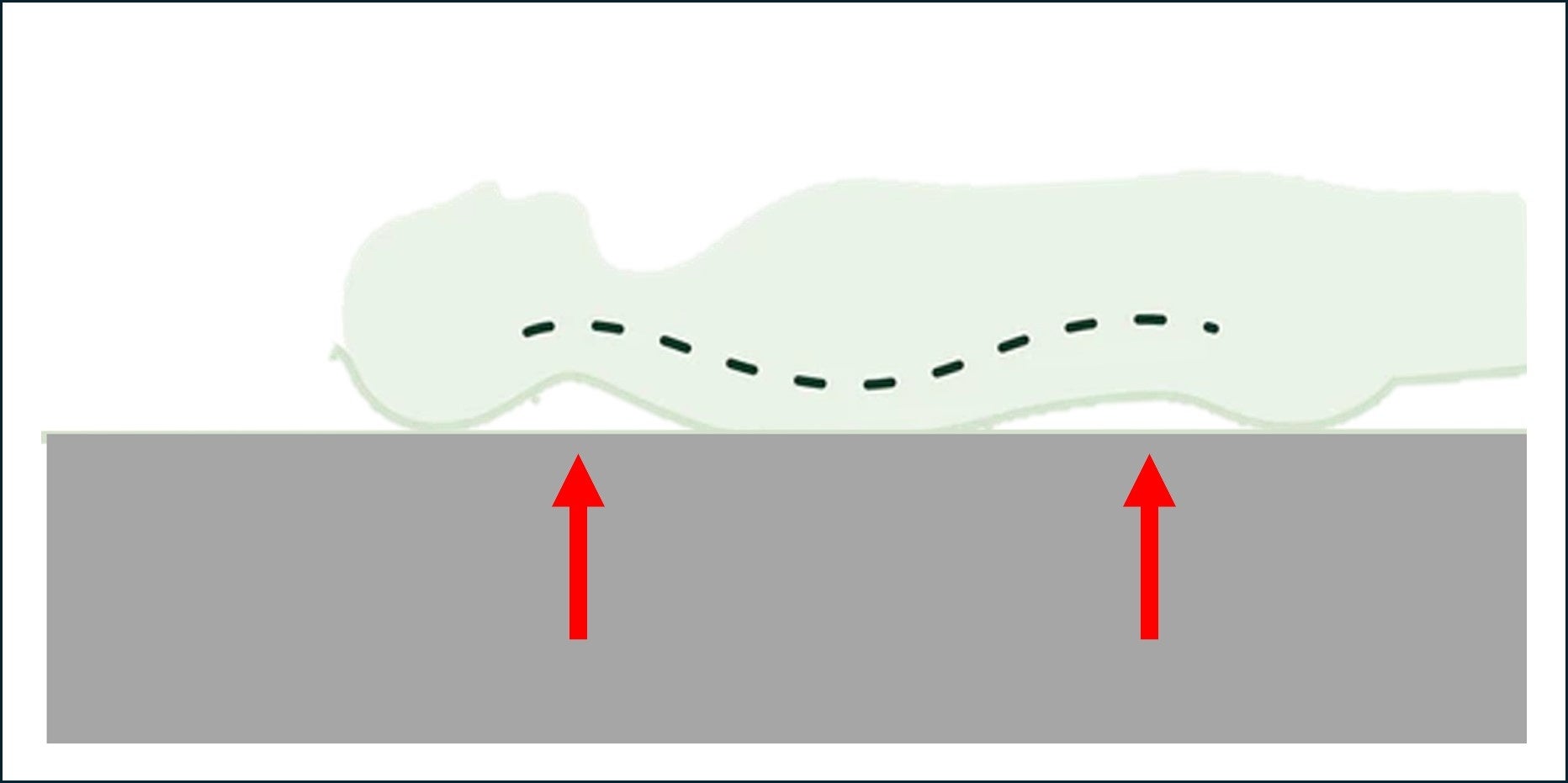
↑ The mattress is extremely hard, so the neck, back and waist are raised.
Conversely, a mattress that is too soft will cause your buttocks, which are prone to body pressure, to sink too much, resulting in a bent-over sleeping position. Also, if your body sinks too much, it becomes difficult to turn over in bed, which promotes blood flow and regulates body temperature, and this can lead to discomfort, among other negative aspects. It also puts strain on your entire body, especially your lower back. While a soft, fluffy mattress tends to give you a sense of satisfaction the moment you lie down, deciding on a mattress based solely on initial comfort could lead to health problems.
Also, while we tend to choose a mattress based solely on our weight and preference for firmness and softness, the mattress that fits us best will also change depending on factors such as our sleeping position and whether or not we have a swayback.
1. Hardness suited to body weight (body pressure distribution)
How to choose a mattress (urethane mattress)
"Newton value" that expresses hardness
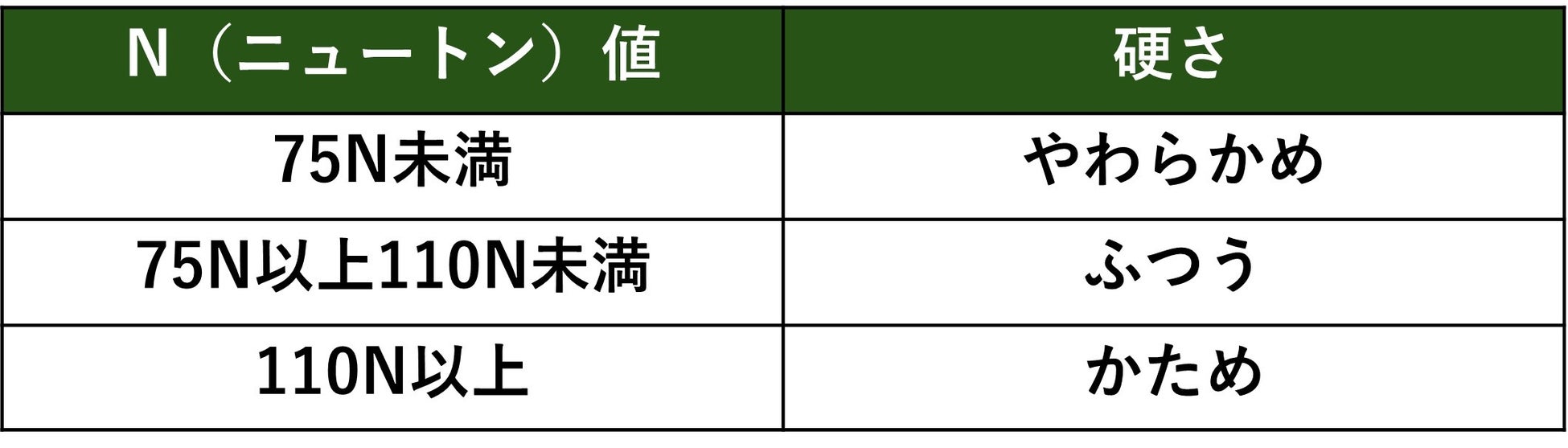
There are clearly defined standards for the firmness of urethane foam mattresses, making it relatively easy to choose one that's right for your body. The "Newton" units listed on mattresses are a unit of measurement that expresses the firmness and resilience of a mattress, and are measured using firmness tests specified by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS). The Consumer Affairs Agency categorizes Newton values into three categories: "soft," "normal," and "firm."
If you're buying online, check the product description.
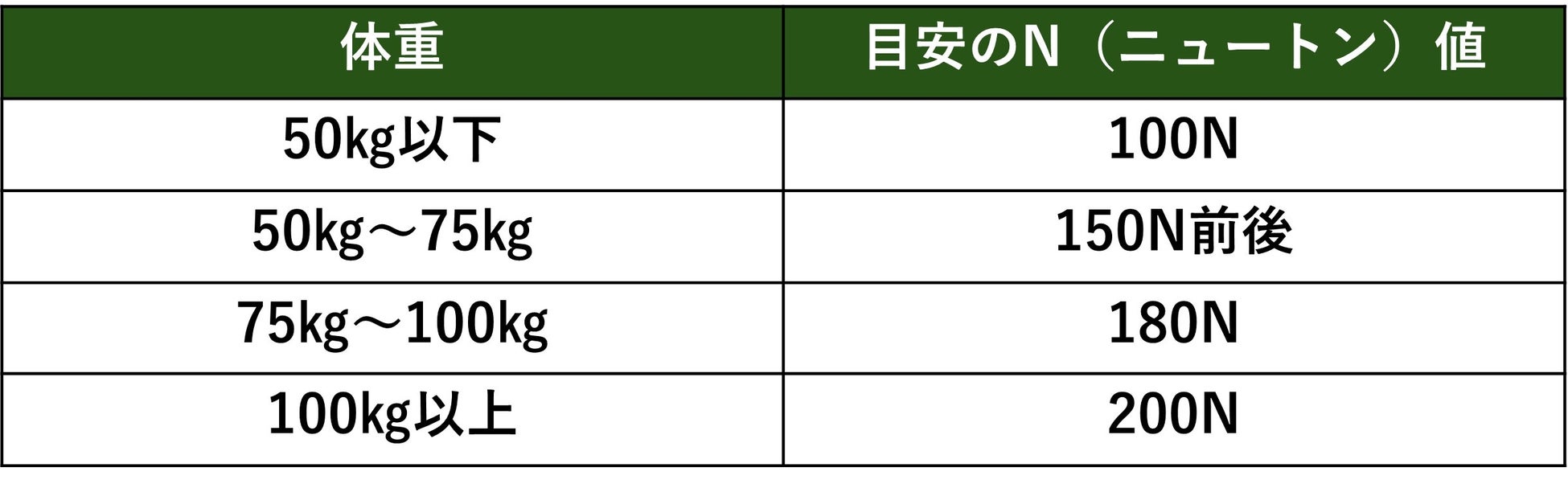
Recommended hardness by weight
The hardness of urethane mattresses varies widely, from 40N to over 200N, but the recommended Newton values based on weight are as shown in the table below.
The ideal firmness varies depending on your body shape and sleeping position.
For example, even if you weigh over 50kg, if you have a swayback or other curvature of the body, we recommend a "softer" mattress. If the mattress doesn't fit well, your back will lift up and put strain on your body.
Additionally, for those who often sleep on their side, a soft, conforming mattress is recommended to reduce strain on the shoulders.
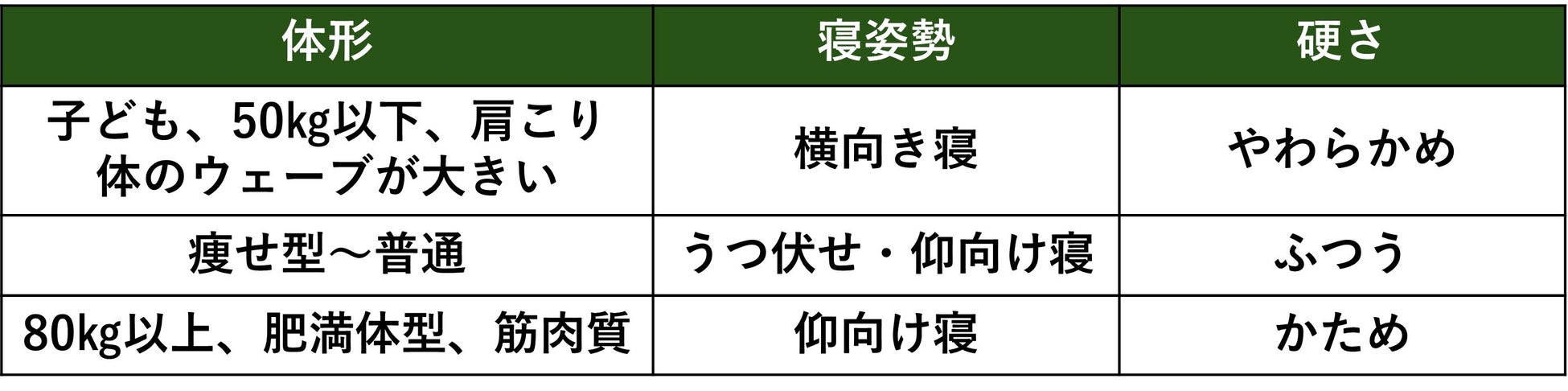
How to choose a mattress (coil mattress)
Hardness is determined by "wire diameter" and "filling"
What is the "wire diameter" of a coil?
The thickness of the coils is called the wire diameter, and the thicker the coil, the firmer the mattress. A wire diameter of 1.7mm or less is considered "soft," around 1.9mm is considered "normal," and 2.1mm or more is considered "firm."
Also, the more coils there are, the softer the mattress will be, while the fewer will be firmer. There are two types of coil arrangement: "parallel arrangement" and "alternate arrangement," with the alternating arrangement being slightly firmer.
Differences in the "filling" of the cushion layer
Coil mattresses are divided into a coil layer and a cushion layer, and the contents of the cushion layer are called "filling."
Coil mattresses have padding between the cover and the coils, which improves body pressure distribution and adjusts the firmness and resilience of the mattress. Because the main material used for the padding is urethane foam, choosing the firmness based on the N (Newton) value mentioned above will make it easier to imagine the overall comfort of the mattress.
This filling should not be too thin or too thick. If it is too thin, you will feel the springiness and it will be uncomfortable to sleep on. On the other hand, if it is too thick, you will not get the benefits of the coils and it will feel similar to a urethane mattress. We recommend a filling thickness of about 5-8cm, which will reduce the springiness and prevent heat buildup.
②Resilience that makes it easy to turn over in bed

Unlike firmness (body pressure dispersion), the degree of bounce is called resilience (rebound elasticity). "Low resilience" and "high resilience" are distinguished by the "rebound elasticity rate," which indicates the resilience. The resilience rate is measured by dropping a copper ball under certain conditions and measuring the percentage of its height after bouncing. The higher the resilience, the more support you will receive when turning over or getting up, making it easier to get a comfortable sleep.
In terms of ease of turning over in bed, people tend to find it easier to turn over on a high-resilience mattress than on a low-resilience mattress. Remember that the "bounce level" is important, as opposed to "firmness."
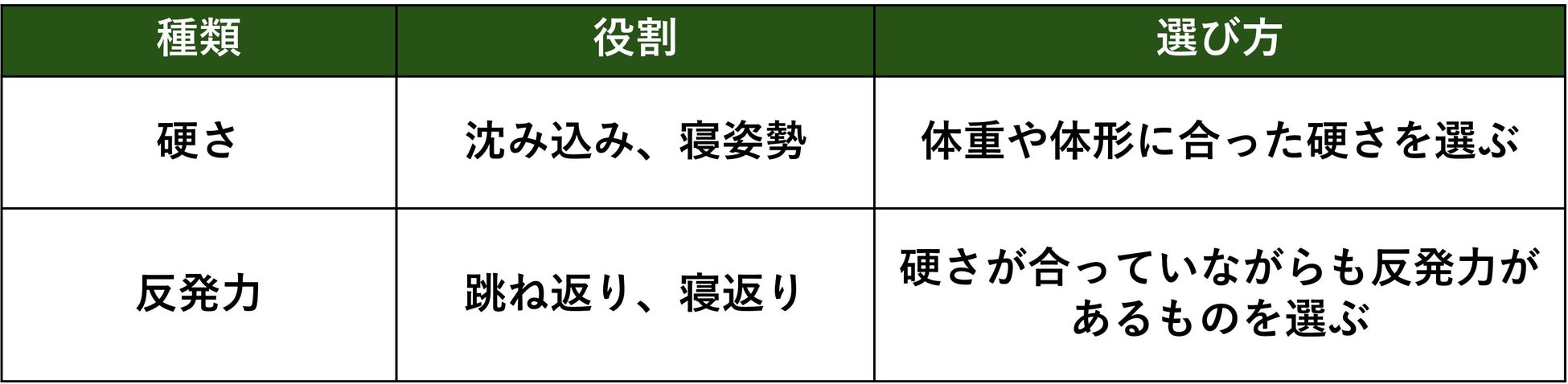
Please refer to the table below to understand the difference between "hardness" and "rebound force." Most manufacturers do not list the rebound elasticity, so if you are concerned, please contact us.
Let's find the ideal mattress for your new life by keeping in mind the key points and precautions of "firmness" and "resilience." Regarding mattresses, which support the widest range of your body, first consider whether they allow you to turn over easily and comfortably. Try out different bedding materials and try them out for yourself.
We are currently hosting a showroom that focuses on the theme of "quality sleep" and takes a fresh look at the bed in which we spend one-third of our lives.
At the "ZINUS POPUP SHOWROOM GINZA," we will be exhibiting a variety of popular ZINUS mattresses, which visitors can freely try out. Other highlights include unique ZINUS products, such as mattresses containing natural green tea ingredients and activated charcoal.
A special event is being held where you can experience a nap in the middle of Ginza (reservations required when visiting), experience ZINUS mattresses, receive free drinks and cosmetics to help you sleep better, check your own condition while sleeping, and choose the mattress that's right for you.
*The special event will run until April 21st (Sun). Gifts will end while supplies last.
ZINUS POPUP SHOWROOM GINZA
Event period: Saturday, February 3, 2024 to Tuesday, April 30, 2024
Venue: Ginza 1-chome Space (1-4-8 Ginza, Chuo-ku, Tokyo)
Opening hours: 11:00-20:00




